SENIORS: This Sleeping Position Raises Your Stroke Risk ⚠️🛏️
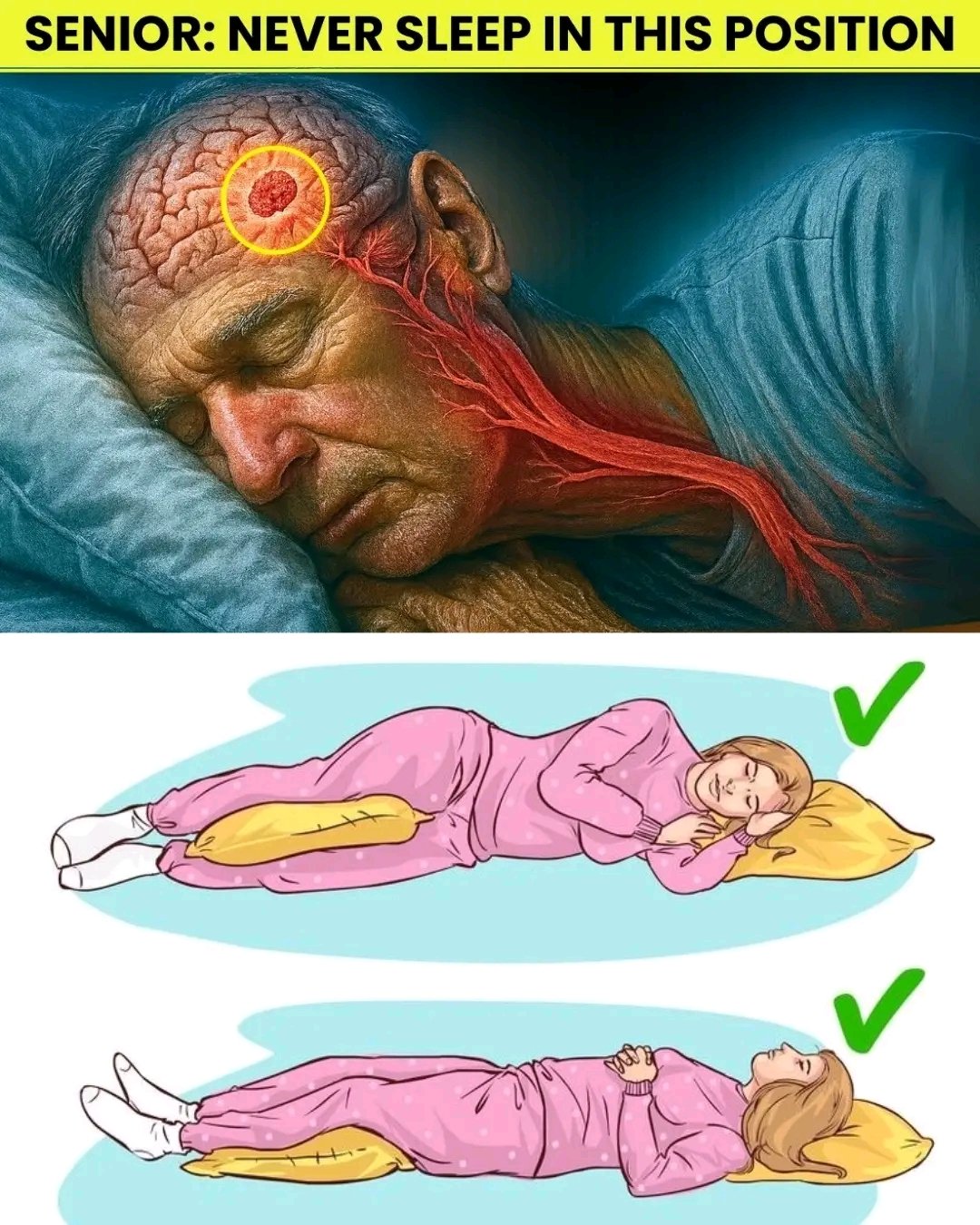
As we age, our sleeping position becomes more important than most people realize. While a good night’s rest keeps your mind and body strong, the wrong sleeping posture—especially for seniors—can increase the risk of stroke, poor circulation, and heart strain. Let’s uncover which position could be harmful and what experts recommend instead.
⚠️ The Risky Sleeping Position: Lying Flat on Your Back
Sleeping flat on your back may seem comfortable, but for many seniors, it can lead to restricted blood flow and increased pressure in the brain and neck. This position can make it harder for blood to circulate smoothly, raising the risk of clots or blockages that contribute to strokes.
In addition, back sleeping can:
- Make breathing harder, especially for people with sleep apnea.
- Increase snoring and reduce oxygen flow during sleep.
- Cause stiffness or pressure in the spine, neck, and shoulders.
❤️ Why Blood Flow Matters
Healthy blood circulation is key to preventing strokes. When blood doesn’t flow properly—due to blocked arteries, pressure on veins, or poor posture during sleep—the brain might not get enough oxygen. Over time, this can contribute to mini-strokes (TIAs) or other vascular problems.
🌙 Safer Sleeping Positions for Seniors
Experts recommend sleeping on your left side for several health benefits:
- Improves circulation and reduces pressure on the heart.
- Supports brain detoxification, helping remove waste through the lymphatic system.
- Promotes better breathing and digestion.
Sleeping on your right side is also acceptable for many people, but it may put slightly more pressure on the heart. The key is comfort and proper alignment—avoid lying completely flat for long hours.
🛌 Helpful Sleep Tips for Stroke Prevention
- Use a supportive pillow to keep your neck and head aligned.
- Elevate your upper body slightly to improve blood flow.
- Avoid heavy meals or alcohol before bed.
- Get at least 7–8 hours of rest every night to allow the body to heal and regulate.
- Exercise regularly, even light stretching or walking, to keep circulation strong.
💡 Final Thoughts
For seniors, sleep isn’t just about rest—it’s a major factor in overall heart and brain health. Avoiding the flat-back sleeping position and switching to your side can lower stroke risk and improve how your body functions overnight.
A few small changes in how you sleep today could protect your health for years to come. 🌙💖
FAQs
1. Is it dangerous to sleep on my back sometimes?
No, occasional back sleeping isn’t harmful, but it’s better to avoid it if you have heart or breathing issues.
2. Does sleeping position really affect stroke risk?
Yes—circulation and oxygen levels are directly influenced by posture.
3. What is the healthiest position overall?
Sleeping on your left side with slight elevation is considered best for circulation and heart health.
4. Can pillows help improve circulation?
Yes—placing a pillow under your knees or between your legs can ease pressure and improve blood flow.






